Było deszczowe sobotnie przedpołudnie, gdy Wojciech Nowak wszedł do małej kawiarenki przy ulicy Marszałkowskiej ze swoją czteroletnią córką, Zosią. Deszcz ślizgał się po chodnikach, a ciche krople uderzające w szyby harmonizowały z pustką w jego sercu.
Kiedyś był człowiekiem pełnym życia. Innowator w branży IT, który zbił fortunę przed trzydziestką, miał wszystko sukces, szacunek, a przede wszystkim miłość. Jego żona, Kinga, była sercem jego świata. Jej śmiech wypełniał ich dom, a jej dobroć łagodziła choćby najcięższe dni. Ale dwa lata temu wypadek samochodowy zabrał ją na zawsze. W jednej chwili kolory zniknęły z jego życia.
Od tamtej pory Wojciech był cichy. Nie zimny tylko oddalony. Jedyną rzeczą, która trzymała go przy życiu, była mała dziewczynka obok niego.
Zosia była żywym portretem matki miękkie kasztanowe loki, jasnobrązowe oczy i ten sam sposób prze# DataFrames
## Creating a DataFrame
We can create a DataFrame in multiple ways:
1. **From a Dictionary**:
„`python
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name’: [’Alice’, 'Bob’, 'Charlie’],
'Age’: [25, 30, 35],
'City’: [’New York’, 'London’, 'Paris’]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
„`
2. **From a List of Lists**:
„`python
data = [
[’Alice’, 25, 'New York’],
[’Bob’, 30, 'London’],
[’Charlie’, 35, 'Paris’]
]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=[’Name’, 'Age’, 'City’])
print(df)
„`
3. **From a CSV File**:
„`python
df = pd.read_csv(’data.csv’)
print(df)
„`
## DataFrame Attributes and Methods
1. **Basic Attributes**:
„`python
print(df.shape) # (rows, columns)
print(df.columns) # Column names
print(df.dtypes) # Data types of each column
print(df.index) # Index range
print(df.head()) # First 5 rows
print(df.tail()) # Last 5 rows
„`
2. **Descriptive Statistics**:
„`python
print(df.describe()) # Summary statistics for numerical columns
print(df.info()) # Concise summary including memory usage
„`
## Accessing and Manipulating Data
1. **Selecting Columns**:
„`python
print(df[’Name’]) # Single column as Series
print(df[[’Name’, 'Age’]]) # Multiple columns as DataFrame
„`
2. **Selecting Rows**:
„`python
print(df.iloc[0]) # First row by integer position
print(df.loc[0]) # First row by index label
print(df[0:2]) # First two rows
„`
3. **Filtering Rows**:
„`python
print(df[df[’Age’] > 30]) # People older than 30
print(df[(df[’Age’] > 25) & (df[’City’] == 'London’)]) # Multiple conditions
„`
4. **Adding/Modifying Columns**:
„`python
df[’Salary’] = [50000, 60000, 70000] # Add new column
df[’Age’] = df[’Age’] + 1 # Modify existing column
„`
5. **Dropping Columns/Rows**:
„`python
df = df.drop(’City’, axis=1) # Drop column
df = df.drop(0, axis=0) # Drop first row
„`
## Grouping and Aggregation
1. **GroupBy**:
„`python
grouped = df.groupby(’City’) # Group by city
print(grouped.mean()) # Mean of numerical columns per group
„`
2. **Aggregation**:
„`python
print(df[’Age’].sum()) # Sum of ages
print(df[’Age’].mean()) # Average age
print(df[’Age’].max()) # Maximum age
print(df[’Age’].min()) # Minimum age
„`
## Handling Missing Data
1. **Detecting Missing Values**:
„`python
print(df.isnull()) # Boolean DataFrame showing missing values
print(df.isnull().sum()) # Count of missing values per column
„`
2. **Dealing with Missing Values**:
„`python
df = df.dropna() # Drop rows with any missing values
df = df.fillna(0) # Fill missing values with 0
df = df.fillna(df.mean()) # Fill missing values with column mean
„`
## Combining DataFrames
1. **Concatenation**:
„`python
df1 = pd.DataFrame({’A’: [’A0′, 'A1′], 'B’: [’B0′, 'B1′]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({’A’: [’A2′, 'A3′], 'B’: [’B2′, 'B3′]})
result = pd.concat([df1, df2], ignore_index=True)
print(result)
„`
2. **Merging**:
„`python
left = pd.DataFrame({’key’: [’K0′, 'K1′], 'A’: [’A0′, 'A1′], 'B’: [’B0′, 'B1′]})
right = pd.DataFrame({’key’: [’K0′, 'K1′], 'C’: [’C0′, 'C1′], 'D’: [’D0′, 'D1′]})
result = pd.merge(left, right, on=’key’)
print(result)
„`
## Time Series Operations
1. **Working with Dates**:
„`python
df[’Date’] = pd.to_datetime(df[’Date’]) # Convert to datetime
df[’Year’] = df[’Date’].dt.year # Extract year
df[’Month’] = df[’Date’].dt.month # Extract month
df[’Day’] = df[’Date’].dt.day # Extract day
„`
2. **Resampling**:
„`python
df.set_index(’Date’, inplace=True)
monthly_data = df.resample(’M’).mean() # Resample to monthly frequency
„`
## Advanced Operations
1. **Pivot Tables**:
„`python
pivot = df.pivot_table(values=’Age’, index=’City’, columns=’Gender’, aggfunc=’mean’)
print(pivot)
„`
2. **Applying Functions**:
„`python
df[’Age_Group’] = df[’Age’].apply(lambda x: 'Young’ if x
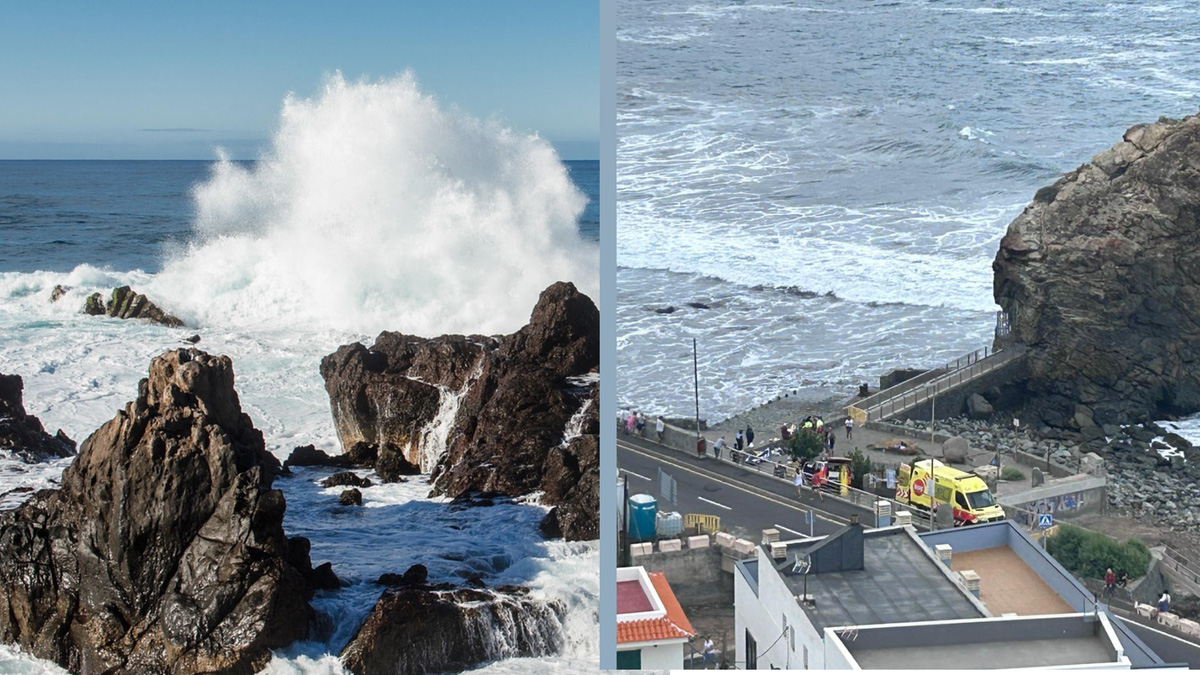


![Karambol na obwodnicy w Rzeszowie. Zderzenie 4 samochodów. Spore utrudnienia [ZDJĘCIA]](https://storage.googleapis.com/bieszczady/rzeszow24/articles/image/92e34d0f-2088-4001-bf55-52ce189cea70)
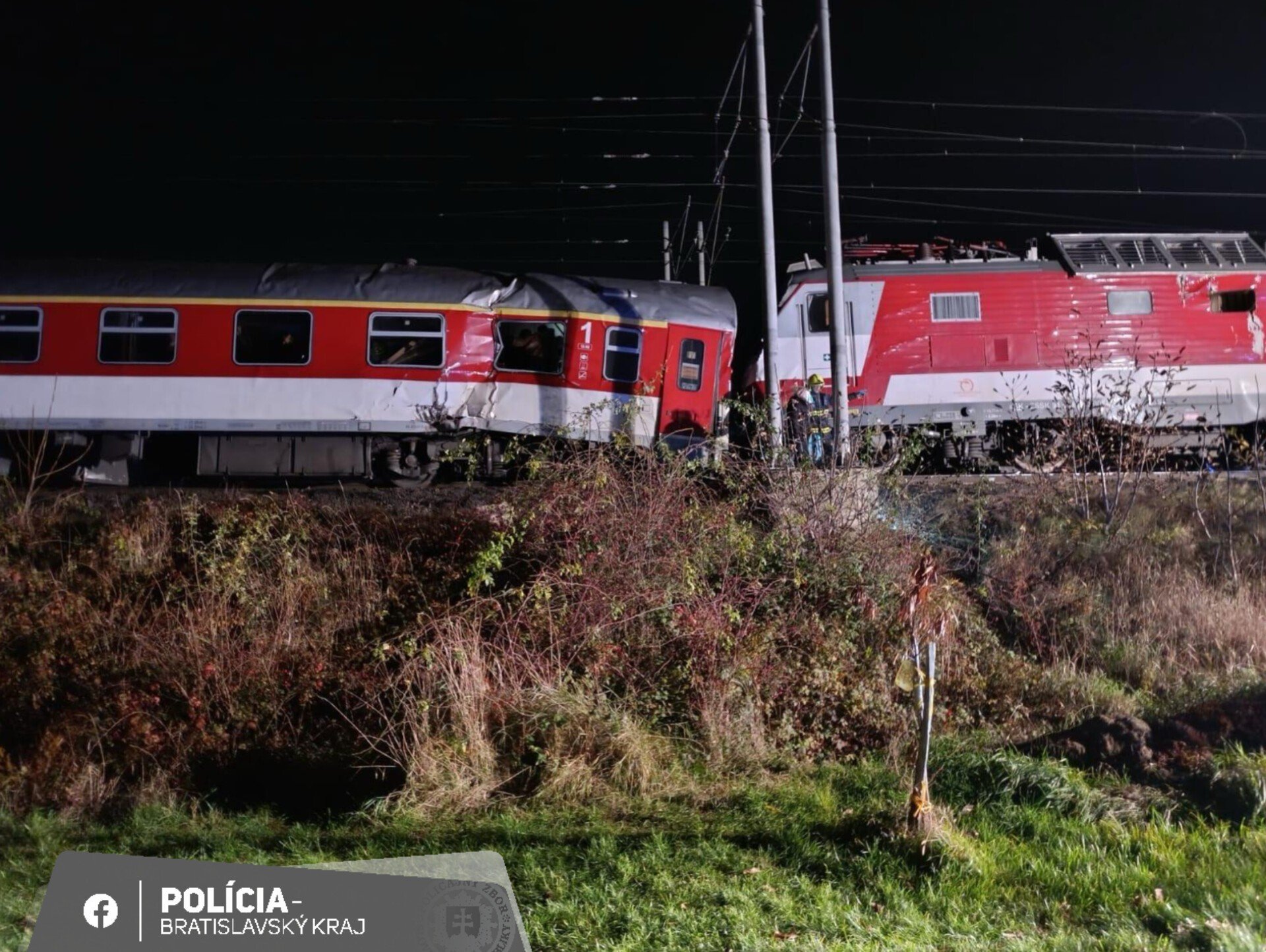







![Są zmiany w kursowaniu autobusów, tramwajów i metra w Warszawie [SPRAWDŹ]](https://images5.polskie.ai/images/2880/35159999/6b5f7b58f8982252cc01d75a07360787.jpg)